In recent years, contradictions have been aggravated between the most powerful states and
economic and political associations (China, the USA, Russia, NATO, BRICS, and others). This trend has spread to comparatively weak, but no less ambitious countries (North Korea, Iran, Israel, Syria, and others). Moreover, the most developed states in their confrontation try by any means to draw into conflict weaker countries, which they can use to achieve their global goals. The emergence, organization, and course of a conflict can be expressed in different forms - from supporting opposition regimes in target countries (for example, Syria) to conducting large-scale military operations (for example, Russia-Ukraine), which, if control is lost, can escalate into a global war.
In a conflict, the active party often initially uses hostile actions against the target country, including a combination of different methods and means to achieve its goals without resorting to a classic military invasion. This type of action is called hybrid warfare. The main elements of hybrid warfare include:
- Information Warfare: Spreading disinformation and propaganda to undermine morale and destabilize society in a target country.
- Support for the opposition and rebels: Arrange support for groups operating in the target country by providing them with financial, material, and consultative assistance and by introducing agents specially trained to carry out “color revolutions.”
- Covert Operations: Difficulty tracking and proving actions, such as sabotage and subversion.
- Cyberwarfare: Attacks on a target country's information and computer systems.
Hybrid warfare is often waged in the “grey zone” between peace and war, making it difficult to determine when the conflict begins and to assign responsibility for actions. However, the hybrid war often escalates into more active military action and turns into war. The main goal of hybrid warfare is to decompose civil society and state structures to such a degree that it allows the interests of the aggressor to be pursued in the quality and quantity necessary for it. Most often, already at the hybrid war stage, significant damage is caused to the country's economy and human losses can also be significant if large-scale civil confrontation is achieved. At this stage, one of the most important destructive factors is the political, social, and moral decline in society, especially among young people, who, due to the lack of life experience, psychological stability, and the inclination towards radicalism inherent in youth, are most susceptible to the impact of factors of a hybrid war waged from outside.
Many wars in human history, and one could say most, have socio-economic factors at their core. Although the causes of wars can be varied and complex, they are primarily about the desire to control resources, territory, and economic advantages. The key aspects are:
- Economic gain: Many wars have been and are being fought to capture or control natural resources such as gold, oil, gas, and other valuable materials.[1] Economic motives often underlie conflicts, even if they are disguised as other reasons.
- Political interests: Territorial expansion and strengthening of political influence are also often associated with economic benefits. Control over new territories can provide access to resources and strategic advantages.
- Trade Interests: Control of trade routes and access to markets is a very common reason for wars in history. For example, the Italian city-states supported the Crusades to control trade routes in the East.
- Religious motives: Although religious wars such as the Crusades often had spiritual goals, they could also include economic and political interests such as control of wealth and territory.
- Social Problems: Wars were sometimes used to solve internal social problems on the aggressor side, such as overpopulation or threats to the ruling elite. Wartime could serve as a means of suppressing internal conflicts and strengthening power.
- Issues of security on the borders of states the creation of buffer security zones, and sometimes the issue of the survival of the state.
 Even military campaigns such as the Crusades, which at first glance had exclusively religious motives: the protection of Christian shrines and pilgrims in Jerusalem from Muslims, had several key reasons:
Even military campaigns such as the Crusades, which at first glance had exclusively religious motives: the protection of Christian shrines and pilgrims in Jerusalem from Muslims, had several key reasons:
- Trade interests: Italian city-states such as Venice and Genoa supported the Crusades to control trade routes to the East.
- Political interests: European monarchs and feudal lords saw the Crusades as an opportunity to expand their possessions and strengthen their political influence.
- Socio-economic factors: Western Europe was overpopulated and the land was scarce, which prompted them to seek new territories to settle and solve the problem of unemployment in their own countries
This region is one of the „hottest“ in the world. Endless wars in recent decades, which have involved a large number of states, including those located outside of this region led to a huge quantity of victims, destruction, humanitarian crises, and the spread of diseases. The number of refugees and displaced persons reaches tens of millions.
Without going into too much history, there has been a serious military standoff between Israel and Hamas. The conflict began with a Hamas attack on Israel in October 2023, which caused significant casualties and destruction. Israel responded with massive airstrikes on the Gaza Strip, which also caused numerous civilian casualties. Continued Israeli attacks forced nearly 2 million Palestinians to flee their homes in the Gaza Strip throughout 2024. At least 220 UN personnel were killed in these targeted Israeli attacks. Nearly 100,000 Lebanese were displaced from their homes in the south of the country due to Israeli shelling. Meanwhile, some 63,000 Israelis were internally displaced from the north of the country due to Hezbollah rocket fire. More than 1 million Lebanese fled their homes in a matter of days amid Israel's invasion and bombing in the end of 2024. The situation remains extremely tense, and experts warn of the possibility of further escalation of the conflict involving Iran and some other Muslim countries.
In the confrontation between Israel and the Arab world, in which Iran, the United States, Turkey, Egypt, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE are actively participating at various levels, in addition to the question of Israel's existence as a state, economic reasons are also visible:
- Resources and Trade: Control over natural resources such as water and oil is an important factor. For example, access to water resources in the region is often a subject of dispute.[2]
- Economic Sanctions and Blockades: Economic sanctions and blockades imposed on Palestine and other Arab countries have a significant impact on their economic development and stability.[3]
- Investment and tourism: The conflict has hurt investment and tourism in the region. In Israel, for example, the mobilization of reservists and the constant threat of violence have reduced the country's appeal to investors and tourists.
- Geopolitical Alliances: Economic interests also influence the formation of geopolitical alliances. For example, the improvement of relations between Israel and some Arab countries, such as the UAE and Bahrain, is due to the economic benefits of cooperation.
 There is significant internal opposition in Israel, especially in the context of the current military operations. The internal opposition includes various political parties, social movements, and civil activists who express disagreement with government policies and military operations. These groups frequently organize protests and demonstrations and are active in public debate and the media.
There is significant internal opposition in Israel, especially in the context of the current military operations. The internal opposition includes various political parties, social movements, and civil activists who express disagreement with government policies and military operations. These groups frequently organize protests and demonstrations and are active in public debate and the media.
Opposition may arise for a variety of reasons, including humanitarian concerns, economic implications, and political disagreements. It is important to note that in a democratic society such as Israel, opposition and public debate are a normal and important part of the political process.
Amnesty Reports International mentions the use of unlawful force to suppress peaceful protests in Israel. Measures can be quite harsh, including detentions of activists, and the use of tear gas and rubber bullets. In some cases, human rights violations such as excessive use of force and restrictions on freedom of speech are also reported.
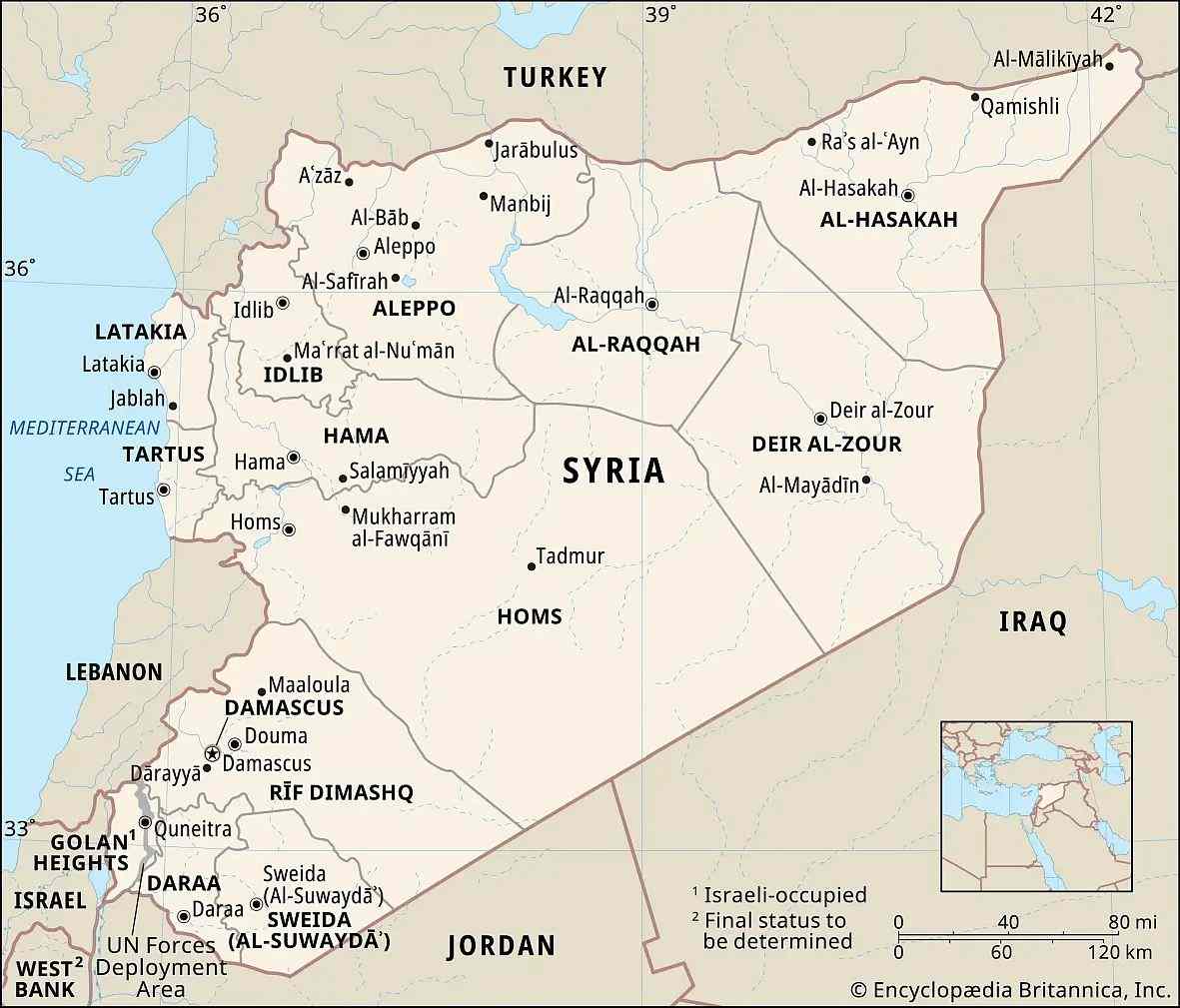
Syria has its oil, natural gas, and phosphates. However, its main problem is its important strategic geographic location - gas pipelines with cheap hydrocarbons from Qatar to Europe can pass through it. Several gas pipeline projects were proposed, for example, from Qatar through Saudi Arabia, Jordan, and Syria to Turkey and then, to Europe. Due to the clash of interests of Turkey, Russia, Iran, the United States, Israel, and the European Union, Syria has been in a protracted civil war for the past decades, gas pipeline projects have not been implemented, and the Syrian economy is destroyed, with huge civilian casualties. In 2013, the Kurdish population in Syria created its autonomy, known as the Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria (AANES), and has an army of 100,000 supported by the United States. The Syrian authorities considered it illegal.
According to the UN Human Rights Office, more than 306,000 civilians have died as a result of the conflicts from 2011 to 2021. According to the UN High Commissioner for Refugees, as of 2021, about 6.6 million Syrians have been forced to flee the country. Most of them have found refuge in neighboring countries such as Turkey (3 million Syrian refugees), Lebanon, and Jordan. As a result of Turkey's active support for the opposition, it attempted a successful armed coup in late 2024. President Bashar al-Assad fled, and Iran's role in this crucial region was lost. Russia's political game is not entirely clear - it is quite possible that, according to secret agreements, Russia has somehow linked the events in Syria and Ukraine in a way that is acceptable to itself. Two Russian military bases remain in Syria, but they do not take part in the hostilities. The armed opposition has seized power, and its future is not entirely clear. Control over the situation in Syria has passed into the hands of Turkey, the United States (oil extraction and refining companies), and Israel, which is waging intense military operations in Syria to create a buffer zone. The number of victims, displaced persons, and economic damage in the recent period has yet to be calculated, but it is likely to be quite significant.
Conclusion: the cause of the tragedy in Syria is the economic and strategic interests of a group of countries, management errors, and the inability of the former Syrian leadership to confront these challenges. As a result, Syria is torn apart and may well cease to exist in its current form.
Iraq. Operation "Desert Storm" (Operation Desert Storm ) was carried out in 1991 by the international coalition led by the United States to liberate Kuwait, which had been occupied by Iraq in August 1990. The main reasons for the operation included economic interests. Iraq, led by Saddam Hussein, invaded Kuwait, accusing it of illegal oil production and demanding the write-off of debts accumulated during the Iran-Iraq War. This move raised concerns in the international community about the stability of the Persian Gulf region and the security of oil supplies. After the liberation of Kuwait in 1991, uprisings broke out in Iraq among Shiites in the south and Kurds in the north, which were brutally suppressed by the government of Saddam Hussein. The scale of Iraqi losses is about 40 thousand people including military force and civilians. Sanctions and destruction caused by the war led to a serious economic and humanitarian crisis.
Conclusion: The tragedy in Iraq is caused by the economic and strategic interests of a group of countries, management errors, and the inability of the former Iraqi leadership to confront these challenges.
Libya. Muammar Gaddafi was overthrown and killed in 2011 as a result of the uprising that became part of the wider protests and revolutions known as the “Arab Spring.” The reasons for his overthrow included his tough authoritarian regime and the uprisings in Tunisia and Egypt, which inspired Libyans to protest against Gaddafi's regime. In March 2011, the UN adopted a resolution allowing the use of force to protect the civilian population, and NATO began airstrikes against Gaddafi's forces, significantly weakening his position. One of the main reasons for Gaddafi's death and the subsequent coup d'état was his advancement and creation of alternative currencies for Africa, which could replace the US dollar and euro in international trade. He proposed creating a gold dinar to be used as a unified currency in African countries. This initiative was part of his broader strategy for strengthening economic independence in Africa and reducing dependency on Western financial systems.
In recent years, there have been several attempted coups in Libya. One of the most significant occurred in 2014 when various armed groups and political factions fought for control over the country. This period was characterized by chaos and instability, leading to the division of the country into competing governments and armed groups. According to some estimates, about 30,000 people were killed as a result of the conflict, and by 2014, the UN estimated that internally displaced persons in Libya numbered around 400,000. Many Libyans also fled to neighboring countries and Europe, seeking security and stability.
Conclusion. The main reasons for the death of Muammar Gaddafi and the subsequent collapse of the country, leading to its subordination to two main political and military forces, were his adventurous international economic policies and the presence of significant oil reserves. Turkey, Russia, Egypt, the United Arab Emirates, Qatar, and Italy are trying to establish an economic and civil order in Libya. The US has also actively participated in Libya's internal affairs, especially after the overthrow of Gaddafi in 2011, conducting operations against terrorist groups such as ISIS and providing humanitarian aid.
Europe
In Europe, the main focus is on the conflict between Russia and Ukraine, in which the United States and most of the European Union countries are actively involved. The main events began on November 21, 2013, when Euromaidan was organized with the active support of external forces, also named the Revolution of Dignity, which led to unconstitutional actions. On February 24, 2022, under various pretexts, Russia began a " special military operation " (SVO). Military actions continue, and both sides suffer significant losses. NATO is strengthening its presence in the region, which also contributes to the growth of tension. Politicians and military personnel in Europe are calling on the population to prepare for a possible escalation of the conflict and predict hard times in European countries. The reasons for the bloody conflict are complex. There are historical factors (many in Russia, including prominent figures like President Vladimir Putin, who have expressed the view that Ukraine is an artificial entity. Putin  has argued that Ukraine was created during the Soviet era and that Russians and Ukrainians are "one people" with a shared heritage), Russia's national security (NATO bases moving closer to Russia's borders), and geopolitical interests (in the form of direct access to the Crimean Peninsula, the operation of gas pipelines to Europe, and Ukraine's desire to join NATO). One of the most important reasons is the presence of a large amount of valuable minerals and extremely fertile lands, which attract the attention of all participants in the conflict. Incidentally, in this regard, Russia is also the subject of close and active (one might say unhealthy) interests of all developed (especially militarily powerful) countries. However, due to Russia's possession of enormous nuclear potential, the only way to get its hands on its natural resources is to collapse the state itself from within. Judging by the events taking place in Russia, they are very well aware of this and undertake extremely harsh countermeasures, which are perceived from the outside as repression, but from the point of view of the state’s survival in the current situation are the only possible ones.
has argued that Ukraine was created during the Soviet era and that Russians and Ukrainians are "one people" with a shared heritage), Russia's national security (NATO bases moving closer to Russia's borders), and geopolitical interests (in the form of direct access to the Crimean Peninsula, the operation of gas pipelines to Europe, and Ukraine's desire to join NATO). One of the most important reasons is the presence of a large amount of valuable minerals and extremely fertile lands, which attract the attention of all participants in the conflict. Incidentally, in this regard, Russia is also the subject of close and active (one might say unhealthy) interests of all developed (especially militarily powerful) countries. However, due to Russia's possession of enormous nuclear potential, the only way to get its hands on its natural resources is to collapse the state itself from within. Judging by the events taking place in Russia, they are very well aware of this and undertake extremely harsh countermeasures, which are perceived from the outside as repression, but from the point of view of the state’s survival in the current situation are the only possible ones.
Ukraine has significant reserves of natural resources, including natural gas, oil, coal, and rare earth metals. [4]These resources are of strategic importance and could be economically beneficial to any country that controls them.[5] Of the 50 strategic minerals critical to the United States, 22 are in Ukraine, including lithium, graphite, and titanium. Of the 34 strategic materials critical to the European Union, 25 can be mined in Ukraine. The reserves of strategic minerals in the territory of Ukraine, which is already under the control of the Russian Federation, are estimated at 6 trillion US dollars!
Fertile lands make Ukraine one of the largest agricultural producers in the world. Control over such resources can significantly strengthen the country's economic position and its influence on the international arena.
Ukraine's losses in this conflict are catastrophic: according to official data from the Ukrainian Armed Forces, 70 thousand were killed and 100-120 thousand were wounded, 5.7 million refugees, 140 thousand buildings were destroyed, agriculture suffered significant losses, and financial losses amounted to hundreds of billions of US dollars.
Conclusion: the main cause of the tragedy in Ukraine is the economic and strategic interests of a group of countries, management errors, and the inability of the Ukrainian leadership to confront these challenges. It is quite possible that after the end of military actions, Ukraine, despite its size and pre-war economic power, will face the sad fate of Syria – it will be torn into pieces and will be under the control of other countries. Considering the enormous external debt of the country, which arose precisely as a result of military actions, this scenario is more than likely.
(insertion as of 2025, 2 March) << Taking into account the meeting of President Trump with Zelensky in February 2025, I have slightly updated the article published in December 2024.
The analysis of the latest events is completely consistent with our predictions regarding the separation of Ukraine. The United States is demanding a larger share of Ukraine's natural resources (in addition to the 2-3 million hectares already for rent) and has resorted to increased pressure on the Ukrainian authorities to achieve this goal. The Europeans, realizing that they were being taken out of the game and a piece of "pie" was snatched from the mouth, became very alarmed, and having gathered together, realizing that they would not be able to take anything away from the United States, decided to continue to put pressure on Russia to force it to give up part of the "pie".
Seeing such a development of events, in the situation of the current division of the world, Turkey also decided to take tough actions against Russia, remembering that Russia took Crimea from Turkey in 1783, and hatching plans to return the territories, when the Black Sea was an internal water body of the Ottoman Empire and Turkey controlled almost its entire coast including Western Georgia (Sukhumi, Batumi) and the southern coast to Trabzon. Taking into account that in this case, the long-term plans of the European Union and Turkey coincide, it is quite possible that, given the current US policy, to increase pressure on Russia, Turkey will be urgently accepted into the European Union. Considering that by squeezing Russia out of Syria and proving its role as a very serious player in the Middle East, possessing the first in terms of training, combat experience, and power army in the region, Turkey's membership in the European Union will be a very serious challenge for the Russian Federation. Turkey will be forced to join all sanctions imposed on Russia. Turkey's trade relations have a large share in Russia's income - a major buyer of gas and oil, a transit route for energy resources to Europe (via the "Turkish Stream"), construction of the Akkuyu NPP, the strategic Bosphorus and Dardanelles straits, a partner that reduces the effect of sanctions.
Turkey's potential membership in the European Union will deal a strong blow to the Russian economy. Such a potential development of events, even subject to an agreement with the United States on the division of Ukrainian territory, will force Russia to concede something to the European Union and Turkey. However, extremely strong pressure on Russia may also lead to harsh military actions against Ukraine and perhaps some European countries.
(end of the insertion) >>
Moldova. Moldova's economic importance for Russia and the EU is not as great as, for example, the importance of major trading partners or countries with large energy resources, but Moldova has strategic importance in several areas. Moldova is located between Ukraine and Romania, and this geopolitical position makes it an important element in the context of Russia's influence on the Black Sea region and Eastern Europe. This is why Moldova's geopolitical stability is also important for Eastern European countries. In addition, Moldova plays a role in the EU's energy strategy, especially in the context of diversifying energy sources and supply routes to reduce dependence on Russian energy resources. The autonomous territorial entity of Gagauzia within Moldova has pro-Russian sentiments, which increases Russia's influence in the region. Moldova is actively seeking integration into the European Union, which will promote European values and standards in the region. This will also open up new opportunities for economic and political cooperation, which irritates Russia. The EU is Moldova's largest trading partner, and a significant portion of Moldovan exports are sent to EU countries.
Moldova has not seen any major armed conflicts in recent years, and the situation in Transnistria remains tense. In 2022, a series of explosions and shelling took place in Transnistria, raising concerns about a possible escalation of the conflict. These incidents were perceived as provocations aimed at destabilizing the region.
In the presidential elections in Moldova in October-November 2024, Maia Sandu won with 52.76% of the vote in the second round. The opposition, represented mainly by the Party of Socialists and its candidate Alexandru Stoianoglo, expressed dissatisfaction with the election results, alleging violations and possible falsifications. The opposition put forward demands for re-elections. Protests and rallies were organized, but international observers recognized the elections as free and fair. The Moldovan authorities used several measures to suppress these protests. Opposition leaders and activists involved in organizing rallies were arrested. The police used tear gas and water cannons to disperse the protesters. The authorities limited the opposition's access to state media and strengthened their control over the information space. New laws were adopted toughening penalties for participation in unauthorized rallies and protests. These measures have drawn criticism from international organizations and human rights activists, who have expressed concern about the violation of human rights and freedom of assembly in Moldova. The political situation in Moldova remains complex and unstable. Despite Maia Sandu's victory in the presidential elections and the successful holding of a constitutional referendum, the opposition continues to express discontent and organize protests. International observers recognized the elections as free and fair, but accusations of violations and falsifications by the opposition persist. Although the authorities are taking steps to maintain order, tensions in society remain high.
Conclusion: the tense situation in Moldova is caused by the economic and strategic interests of a group of countries. Stability in Moldova depends on the ability of the new leadership to confront these challenges.
South Caucasus
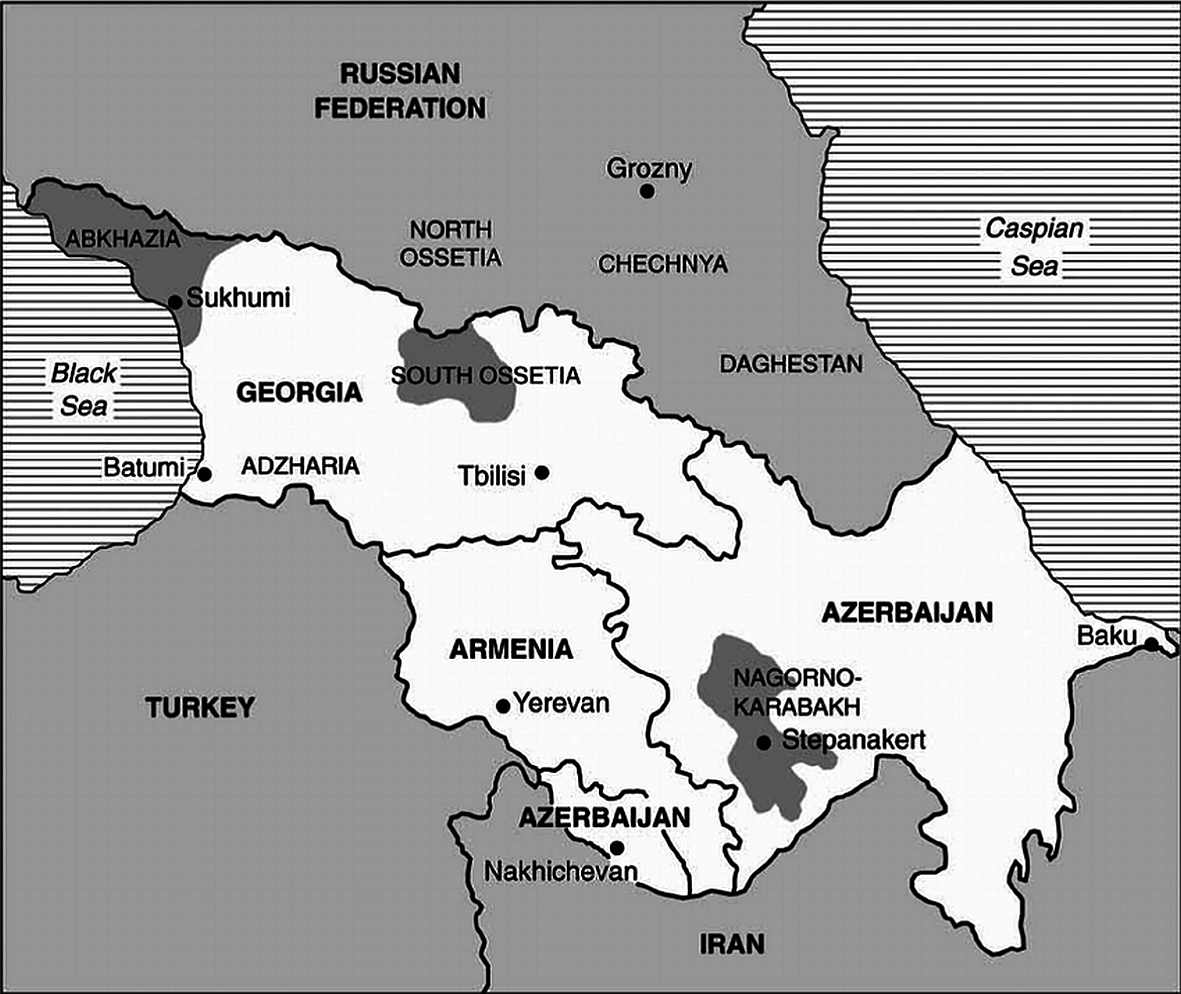
Tensions remain high in the Caucasus, particularly in Nagorno-Karabakh, where armed clashes between Armenian and Azerbaijani forces occur periodically. Despite ceasefires, the conflict remains unresolved, with both sides continuing to accuse each other of violating agreements. Ethnic problems and territorial claims are at the forefront of the conflict. However, the average observer often does not notice that economic factors also play a significant role in the conflict for Upland Karabakh. Some key aspects:
- Region-rich natural resources, including useful fossils and aquatic resources. Control over these resources and infrastructure is strategic meaning for both sides.
- Upland Karabakh and the surrounding areas are important for the creation of transport corridors that can connect Azerbaijan with Nakhichevan and Turkey. This may significantly improve economic integration and trade in the region.
- Azerbaijan strives to develop infrastructure and economy on returned territories that may contribute to growth and stability in the long term.
Turkey, Russia, and Iran are important external players in this conflict, although France and the United States also have a significant interest.
Conclusion. In Armenia, a lot of people perceived the results of the conflict as a tragedy and defeat. Armenia lost the support of its main ally – Russia, which weakened its position in the international arena and has affected Iran, which is seeking rapprochement with Azerbaijan. Armenia is forced to seek new allies. The conflict is based not only on territorial claims but also on economic interests.
 Georgia, similar to Syria, has an important geopolitical location for the entire vast region where the interests of China, Iran, Turkey, Russia, and other countries converge, and is also facing the danger of being drawn into a full-scale military conflict (the fourth in the last 35 years), this time threatening the complete collapse of the country. In Georgia, large-scale protests are taking place at the end of 2024, aimed at overthrowing the current government. The conflict involves, on the one hand, four opposition parties that entered the country's Parliament in 2024, and, on the other hand, the Georgian Dream party, which has got the majority of seats in Parliament. The leaders of the opposition parties, with the support of the former President of the country S. Zurabishvili, were able to attract part of the population to their side, including part of the intelligentsia and students. The United States and most of the European Union countries are openly participating in supporting the opposition. As mentioned above, about the substitution of real goals with far-fetched pretexts, support for the opposition forces is carried out under the slogans of unproven violations of the parliamentary elections on October 26, 2024, ridiculous accusations of adopting laws on Transparency of foreign influence, and limiting LGBT propaganda and, taking this into account, of Georgia's rollback from the democratic path of development. The majority of non-governmental organizations (NGOs) [6], their employees, and family members, as well as some private universities in Georgia, and businesses were on the side of the opposition movement. Several diplomats, including the Georgian ambassadors to the Czech Republic, the United States, Lithuania, and Bulgaria, resigned in protest against the government's decision to temporally freeze the European integration process. Several high-ranking officials of the Ministry of Internal Affairs resigned, including the head of the operational planning department of the special assignments department.
Georgia, similar to Syria, has an important geopolitical location for the entire vast region where the interests of China, Iran, Turkey, Russia, and other countries converge, and is also facing the danger of being drawn into a full-scale military conflict (the fourth in the last 35 years), this time threatening the complete collapse of the country. In Georgia, large-scale protests are taking place at the end of 2024, aimed at overthrowing the current government. The conflict involves, on the one hand, four opposition parties that entered the country's Parliament in 2024, and, on the other hand, the Georgian Dream party, which has got the majority of seats in Parliament. The leaders of the opposition parties, with the support of the former President of the country S. Zurabishvili, were able to attract part of the population to their side, including part of the intelligentsia and students. The United States and most of the European Union countries are openly participating in supporting the opposition. As mentioned above, about the substitution of real goals with far-fetched pretexts, support for the opposition forces is carried out under the slogans of unproven violations of the parliamentary elections on October 26, 2024, ridiculous accusations of adopting laws on Transparency of foreign influence, and limiting LGBT propaganda and, taking this into account, of Georgia's rollback from the democratic path of development. The majority of non-governmental organizations (NGOs) [6], their employees, and family members, as well as some private universities in Georgia, and businesses were on the side of the opposition movement. Several diplomats, including the Georgian ambassadors to the Czech Republic, the United States, Lithuania, and Bulgaria, resigned in protest against the government's decision to temporally freeze the European integration process. Several high-ranking officials of the Ministry of Internal Affairs resigned, including the head of the operational planning department of the special assignments department.
The latest protests have focused on the demand for repeat parliamentary elections, as the opposition does not recognize the October 2024 elections as legitimate. The opposition parties overall won the following: Georgian Dream: 53.93% of the vote (89 seats), Coalition for Changes: 10.92% of the vote (18 seats), Unity - National Movement: 10.12% of the vote (17 seats), Strong Georgia: 8.78% of the vote (14 seats), Gakharia - For Georgia: 7.76% of the vote (12 seats). The remaining parties won less than 5% of the vote and did not make it into parliament.
The elections were observed by 529 representatives from 42 countries. The OSCE/ODIHR published a report on the parliamentary elections, which, despite the vagueness of the content, contains information that there were certain violations of the electoral process, although their statistics are not provided. The reader must conclude for himself that with the participation of more than 2 million voters and the presence of, say, 200 violations - this is 0.01%, which obviously should not be a reason for demands for repeat elections. The most important conclusion in the report is the fact that, apart from the description of some facts of violations, no conclusion is given about the desirability or necessity of repeat elections. And in this sense, the Georgian Dream party is right - according to the presumption of innocence, the burden of proof of guilt lies with the accuser. However, the former President of Georgia, S. Zurabishvili, ignoring the OSCE/ODIHR conclusions unfavorable to the opposition, stated that the conclusion of international observers contains information about violations during the elections. In conclusion, she called for the continuation of the confrontation under any circumstances and this confrontation must end with the removal of the current government, the annulment of the results of the elections, and the holding of repeat elections as many times as until a coalition of opposition parties is elected to the parliamentary majority.
The same is instilled in the youth and those layers of civil society who are not inclined, lazy, or unwilling to independently analyze the available facts and draw their conclusions, not imposed by someone. It is quite obvious that such an unconstructive position will ultimately lead to a sharp confrontation, which may spill over into civil society, which, with the support of external interested forces, will result in an armed conflict and, if sensible leaders are not found, a civil war with all the ensuing consequences in the form of victims, destruction, economic collapse, loss of statehood and the coming to power of representatives of organizations and associations interested in the collapse of the country (including foreign ones).
As already mentioned, currently humanity is in the phase of revising the world order of relations between states, changing borders and economic relations. Even such major associations as the EU will change politically shortly and will seek new economic incentives. Georgia is also going through an extremely tense historical moment - all four countries bordering it are in a military confrontation: Azerbaijan-Armenia, Russia-Ukraine, Turkey-Syria. Turkey's successful actions in Syria have moved it to the level of the strongest player in the Middle East. Given these events and some of the moods of the Turkish political elite, it can be assumed that when Turkish leaders talk about expanding control over territories historically associated with the Ottoman Empire, they mean regions that were once part of the Ottoman Empire and where Turkey seeks to strengthen its influence. In light of the aggravation of relations between Moscow and Sukhumi, it is quite likely that Turkey will want to annex the unrecognized Abkhazian Republic and it will become a Turkish province. The large penetration of Turkish business into the Adjara Autonomous Republic of Georgia should cause great concern. Let us remember the existence of the strategy of "soft power".
The huge population of Georgia’s close neighbor - Iran, in the event of a brutal military strike by Israel and the United States caused by Iran's nuclear ambitions, will try to rescue. Millions of refugees will flood into neighboring countries, and from many points of vie,w the most attractive country for them is the territory of Georgia.
Naive readers may frivolously object that such a scenario is impossible, but if we recall the recent past when Georgians in Abkhazia were slaughtered like chickens in the backyard, football was played with their heads and tens of thousands fled through mountain passes on foot and not all of them made it alive - no one believed in this in advance either.
Conclusion.
The scope of this article does not provide for consideration of numerous examples when external forces, to seize the resources of countries in many regions of the world, using methods of hybrid warfare, or even direct armed intervention, tried to destroy legitimate political regimes and ruined these countries. Information on this topic can be easily found on the Internet. This article shows, using several examples (an interested reader can check the facts provided in open sources on the Internet), that humanity has entered a period of rapid and large-scale geopolitical changes, which are mainly caused by economic reasons. Due to the rapid technological development of humanity and competition for the possession of depleting natural resources and markets, these reasons tend to escalate and push participants into a "hot phase". In such conditions, small countries that can be easily and casually crushed in the interests of the "heavyweights" must show greater political flexibility in foreign relations and, at the same time , closely monitor and actively prevent hostile actions of external players aimed at internal destabilization in such countries. The population of these countries must have constant, objective, and reliable information support about the events taking place. Prevention of phenomena threatening the stability of the state is very difficult and depends on a huge number of difficult-to-predict and control factors. Some of them, although they are obvious and easy to use, for example, force methods, are not effective in the long term. Others, such as raising the level of consciousness of the population, require special technologies and professionally trained specialists in this field (for example, lecturers at universities or representatives of the mass media) and are stretched out in time - they must be carried out constantly. There is a category of factors that are generally difficult to control. For example, as of October 2024, Georgia accepted 27 thousand refugees from Ukraine (in reality, there are many more) who received humanitarian status precisely due to the support of the current government. Many of these people are now in the ranks of the opposition, taking part in actions directed against the current government. Another example is the participation of some European parliamentarians who are on an official visit to Georgia and taking part in street protests in the ranks of the opposition. Such factors, of course, are difficult to foresee and quite difficult to counteract. Some factors fall within the competence of the internal security agencies, which are guided by laws and instructions. They are focused on those whom Mahatma Gandhi often spoke about, referring to the importance of independence and self-sufficiency for India: "The most dangerous enemy is not the colonizer and occupier, but your compatriot, "fed” by the occupier."
[1] https://ru.fusedlearning.com/8-main-reasons-war
[2] https :// news . harvard . edu / gazette / story /2024/02/ looking - at - causes - measuring - effects - of - israel - hamas - war /
[3] https :// www . focus - economics . com / blog / the - hamas - israel - conflict - economic - implications /
[4] https://www.cbc.ca/news/politics/natural-resources-ukraine-war-1.6467039
[5] https://www.businesstoday.in/latest/world/story/are-ukraines-vast-natural-resources-a-real-reason-behind-russias-invasion-323894-2022-02-25
[6]There are about 32 thousand registered non-governmental organizations (NGOs) in Georgia, but only about 3,700 of them are actively functioning.

 Simon Japaridze, who led all important ascents of Kavkasioni in 1926-28, initiated researchers into the study of the
Simon Japaridze, who led all important ascents of Kavkasioni in 1926-28, initiated researchers into the study of the